Welcome to Part 5 of Calculator Tricks
Part 5 will cover:
* Solving 2 by 2 equations
* Finding roots of the quadratic equations
The above tasks will be accomplished by using a simple calculator. That means we have only the arithmetic functions, square roots, percents, and memory to work with.
Solving 2 by 2 Equations
Suppose we are assigned the task solving for x and y:
Ax + By = E
Cx + Dy = F
This is a system of two simultaneous equations with two unknowns, x and y. We can use matrices to visualize this problem:

Take the inverse of the coefficient matrix and left multiply both sides to get:

We can find the inverse of the coefficient matrix by:

The product A × D - B × C is called the determinant. Finally, we solve for x and y:

Now that we have our general solutions, how do we tackle this on a simple calculator?
2 × 2 System of Equations
We only have one memory in the register to work with. Here is a strategy:
1. Calculate the determinant. Keystrokes: A × D - B × C =. Note this number down on paper. The calculator's memory will be required to find x and y.
2. Solve for x. Use the sequence:
MC
D × E = M+
B × F = M-
MR ÷ determinant =
3. Solve for y. Use the sequence:
MC
A × F = M+
C × E = M-
MR ÷ determinant =
---------------
Example: Solve the System
2x + 3y = -1
x - 3y = 2
We have A = 2, B = 3, C = 1, D = -3, E = -1, F = 2
Step 1:
Keystrokes:
MC
2 × 3 +/- = M+
3 × 1 = M-
MR
The determinant is -9. Write this result down.
Step 2:
Keystrokes:
MC
3 +/- × 1 +/- = M+
3 × 2 = M-
MR ÷ 9 +/- =
x ≈ 0.3333333
Step 3:
Keystrokes:
MC
2 × 2 = M+
1 × 1 +/- = M-
MR ÷ 9 +/- =
y ≈ -0.5555555
----------------
Solving Quadratic Equations
Let's tackle on how we find the roots of the equation:
Ax^2 + Bx + C = 0
Our focus for this blog entry will be finding real roots.
Referring to the quadratic formula:

We can derive our algorithm for finding both roots:
1. Calculate the discriminant. Store this result in the calculator's memory.
Keystrokes:
MC
B × = M+
4 × A × C = M-
2. Find the first root:
Keystrokes:
MR √ - B ÷ 2 ÷ A =
3. Find the second root:
Keystrokes:
MR √ +/- - B ÷ 2 ÷ A =
---------------
Example: Find the roots of
x^2 + 5x - 6 = 0
Let A = 1, B = 5, and C = -6
Step 1: Discriminant
MC
5 × = M+
4 × 1 × 6 +/- = M-
Discriminant = 49
Step 2: First Root
MR √ - 5 ÷ 2 ÷ 1 =
One of the roots is x = 1.
Step 3: Second Root
MR √ +/- - 5 ÷ 2 ÷ 1 =
The other root is x = -6
I hope this series is helpful. This series has showed how to make various calculations with a simple calculator: arithmetic procedures including fractions, area of a circle, distance between two points, calculating the total shopping bill, solving 2 x 2 simultaneous equations, and solving quadratic equations.
Until next time,
Eddie
This blog is property of Edward Shore, 2012.
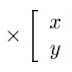 Reviewed by Anonymous
on
14:40
Rating:
Reviewed by Anonymous
on
14:40
Rating:






No comments: